Consumption of electric cars: This is how much electricity they will consume in 2024
How high is the electricity consumption of electric cars?
If you want to buy an electric car, you inevitably ask yourself how high the power consumption of vehicles with this type of drive is. And how well do the electric cars compare to classic gasoline and diesel engines? Consumption can vary greatly depending on the model. According to the manufacturer, the consumption values are between 13 and 25.2 kWh per 100 km. While the Fiat 500e with the smaller battery is one of the most economical electric cars, at least on paper, the Jaguar I-Pace occupies the negative top spot.
The average consumption of electric cars is estimated at 15 kWh per 100 km, a value that can only be achieved in city traffic with many models. In practice, the actual value often differs because it is influenced by many factors. Therefore, as with the combustion engine, it is not possible to make a blanket statement about how high the consumption of an electric car will be.
What factors influence e-car consumption?
Whether an electric car is economical depends on several factors. The amount of electricity required is of course significantly influenced by the drive. Depending on how efficiently the electric motor uses the energy fed into the grid, the electricity consumption is higher or lower.
E-cars that have a long range due to a particularly large battery are not necessarily more economical. Passenger cars that are equipped with significantly smaller batteries in comparison also achieve long ranges. The ADAC Ecotest certified this to the Hyundai Kona and the electric version of the Kia Niro, among others.
When tapping electricity, charging losses are generally incurred. This means that not all of the energy provided by the charging station reaches the battery. The amount of charging losses varies depending on the vehicle, the temperature conditions and the nature of the charging points. They can be considerable in some cases. They are comparatively high, especially for DC fast charging.
To completely fill the 105 kWh battery of a BMW iX, for example, 125.2 kWh must be charged. In the Tesla Model 3, the 82 kWh battery must be supplied with about 92.2 kWh to bring the charge level of the battery to 100 percent.
You can also influence the power consumption of the electric vehicle with your personal driving behavior. If you approach the traffic lights with foresight and let the vehicle roll out slowly instead of bringing it to a standstill with the brake pedal, you will consume significantly less energy and even recover it.
Unlike gasoline and diesel vehicles, the kinetic energy of the moving car does not go unused in electric cars when braking. In electric cars, so-called recuperation ensures that the energy is converted into electrical current when coasting and then fed into the battery. The electric motor serves as a generator. This increases the range of the electric car.
Large temperature differences, on the other hand, can severely affect the range. Since the electronics work less efficiently during frost, the power consumption for e-cars is higher in winter. If you drive at high speeds, consumption increases at the same time, as with the combustion engine. It rises with increasing speed.
E-cars: Consumption and range depend on this
-
Battery: The greater the usable capacity of the battery, the more electrical energy the battery can absorb. If the car also has an efficient drive and good aerodynamics, a large battery is a guarantee for a decent range.
-
Efficient drive: Economical e-cars can cover a greater distance with the same amount of electricity. That's why it's not just the sheer size of the battery that is important, but also the most efficient drive components possible. But it is not only the electric motors that have a major influence. Also important is the inverter, which converts the direct current from the battery into alternating current for the motors and at the same time regulates the drive.
-
Speed: Speed affects power consumption. The faster you drive, the more the car consumes and the more the range shrinks.
-
Handling: If you drive your electric car with foresight and rarely step on the brakes, especially in city traffic, energy is recovered when decelerating with the help of recuperation and fed into the battery. The side effect: The brake system is less stressed in an electric car. Therefore, the brake discs and brake pads need to be replaced less often.
-
Driving distance: Partly due to recuperation, the power consumption of electric cars in urban regions is usually significantly lower than for frequent country road and motorway journeys.
-
Additional power consumers: In addition to the drive, comfort features such as seat heating, air conditioning or windscreen heating also require energy. If they are switched on, this is also at the expense of range to a small extent.
-
Temperature: Winter temperatures affect the efficiency of the drive. But the battery also works best between 20 and 40 degrees. At lower temperatures, charging processes also take more time, which is why the battery can be preheated in many modern electric cars. The bottom line is that electric cars are more efficient in summer than in winter.
-
Charging losses: Losses incurred when charging electric cars are automatically counted. Therefore, it makes sense to include them in consumption from the outset.
-
Aerodynamics: How efficiently a car drives also depends on the shape of the body. Vehicles with a small frontal area offer lower air resistance and are therefore much more economical. Due to the range problem, the optimization of aerodynamics in the development of electric cars is once again much more important than for combustion engines.
-
Tyre type and tyre pressure: If the tyre pressure is too low or too high, the behaviour of the tyres on the road changes. Rolling resistance increases, which goes hand in hand with increased power consumption. With the right tire pressure and the special tires for e-cars, on the other hand, you can minimize rolling resistance and drive more economically.
Calculate electricity costs for an electric car: Here's how it works
Due to the many influencing factors, it is very difficult to calculate the exact electricity consumption for an electric car. However, with the help of a simple formula, you can determine the price of electricity per kilometer. To do this, multiply the current price for a kilowatt hour by the consumption per 100 kilometers. With an electricity price of 0.36 cents and a consumption of 12 kWh, this would be 4.32 euros per 100 kilometers. Charging losses must also be taken into account, as well as the costs for wallboxes and the like. In addition, the price of charging electric cars at public stations can vary greatly. Some providers charge according to the amount of energy charged, while others charge according to the charging time. In addition, there are providers with package solutions.
Real costs of electric cars: electricity consumption and more
In order to determine how electric cars compare to gasoline and diesel cars, you should not only look at the purchase price and energy costs. Regular maintenance costs such as insurance, maintenance or any repairs are also part of the calculation. A plus for e-cars: the maintenance costs are lower. And the high subsidies for e-cars from the state also reduce the acquisition costs for electric vehicles. Up to 4,500 euros in subsidies are possible for purchases in 2024.
This is why electric models often perform better in terms of total costs compared to classic combustion engines. Cheap electric cars that are inexpensive to maintain are therefore no longer a rarity. With the Citroën e-C3 and the Dacia Spring, two models have been presented that are also cheap to buy.
Range ranking: Which electric car consumes how much?
When it comes to ranges according to the WLTP standard, there are now quite a few electric models that can travel 500 kilometers or more on a single battery charge. These include, for example, the Mercedes EQS with a range of up to 782 kilometers or the Polestar 2 Long Range Single Motor, which covers up to 654 kilometers on a single battery charge. Although the value may differ in practice, models with a large battery are usually at the top of the rankings. However, as the ADAC Ecotest proves, the results are far more differentiated when power consumption, battery and range are considered together.
The automobile club has subjected modern electric cars of different price ranges and sizes to a reality check in a series of tests. In the test vehicles charged with alternating current, the results showed large differences in consumption. The most economical electric car was the Hyundai Ioniq Electric, which is now only available as a used car. According to the test, it consumes 16.3 kWh per 100 km. Power guzzlers such as the Mercedes EQV or the Audi e-tron 55 quattro draw at least 25 kWh from their batteries for 100 kilometers, but this is of course also due to the vehicle size, weight and body shape.
Find the right electric car with these search filters on mobile.de
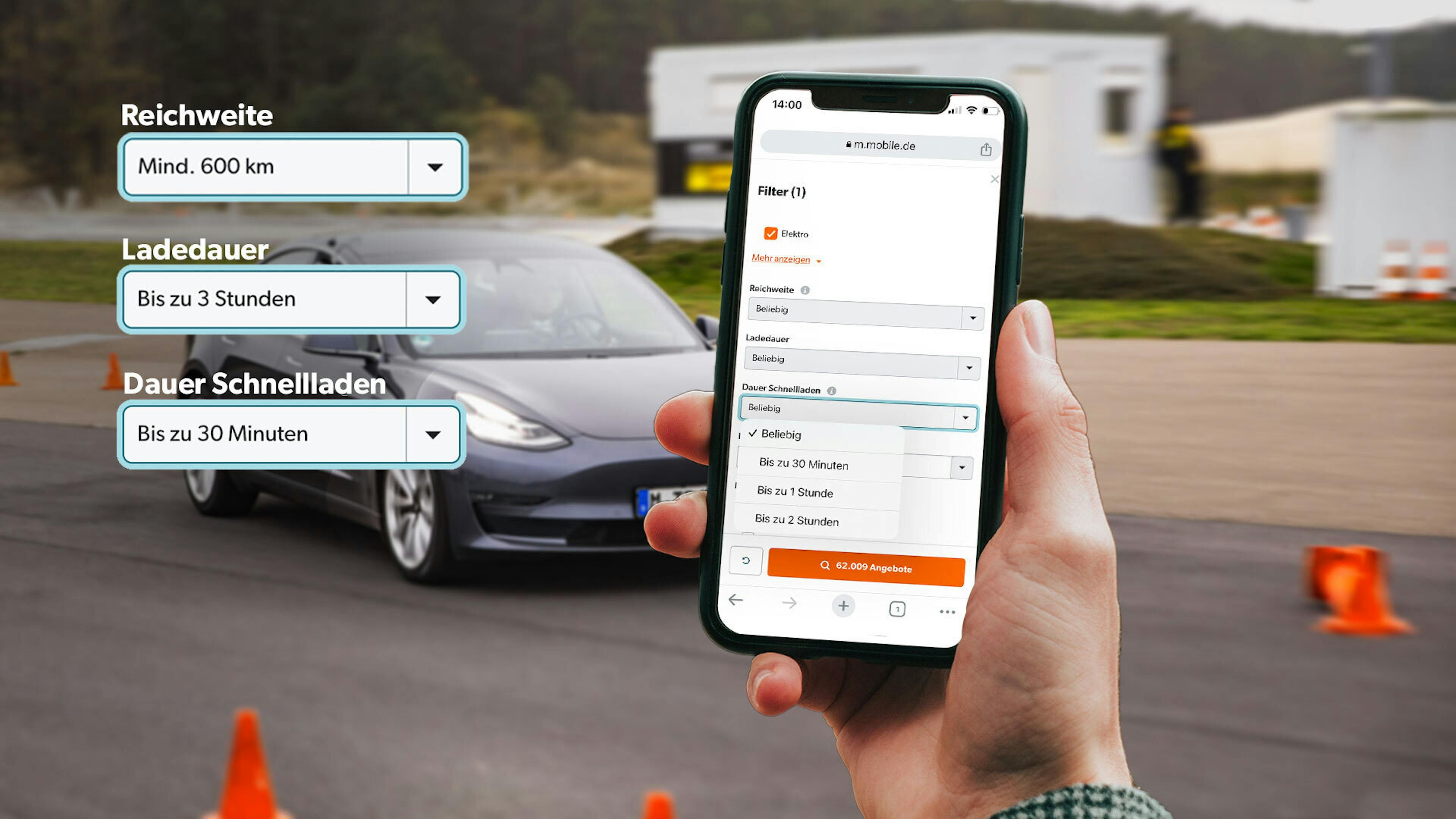
On mobile.de, there are new filter options that make it easier for you to find the right electric car. If you select "Electric" as the fuel type in the other filters of the desktop version of the portal, a new submenu with additional tabs will pop up. When searching for your desired electric car, you can now set the desired minimum range, as well as limit the charging time at conventional charging points and fast charging stations. On the advertisement page of the respective vehicles, the plug type is now also displayed.
You can also specify how large the battery capacity of the electric car should be. Since some manufacturers rent or lease the batteries of their e-cars separately from the actual vehicle, you can choose whether the battery should be included in the purchase or whether you want to rent it. You can also set that you are looking for a car without a battery.

Posting Komentar untuk "Consumption of electric cars: This is how much electricity they will consume in 2024"